SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificates are network protocols that have been adopted as the standard for encrypting data when connecting between a browser and a server hosting a website. These certificates are also used to encrypt other types of transmissions, such as email, FTP connections, and so on.
Internet users typically don’t pay attention to the different types of certificates; the presence of a “green padlock” next to the website’s address is often enough for them. In this article, we will try to explain the methods by which certificates are actually encrypted.
What Is RSA?
RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman algorithm) is a data encryption mechanism invented in 1978. It was the first fully asymmetric encryption algorithm. Its characteristic feature is the use of two keys: a public key for encrypting data (which can be known by anyone) and a private key for decrypting data (which should be protected from unauthorized access).
What is ECDSA?
ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm) is a more modern version of a cryptographic algorithm developed in 1999. It also relies on a private and public key, but the key lengths are shorter. The difference in key length is visible in the image below.
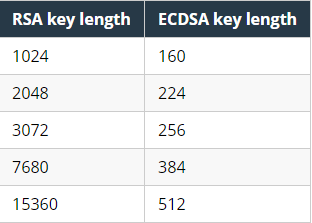
Despite the reduction in key length, the level of security remains the same as with RSA keys.
An additional advantage of certificates with an ECDSA key is speed. When establishing a connection with a server, it performs faster, which can make the website load a bit quicker. It’s also worth noting that ECDSA keys have been positively approved by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the National Security Agency (NSA).
How SSL certificates work
Both encryption algorithms are based on the creation of two keys:
- Public key: This key can be known by anyone and is used only for encrypting data. Knowing this key will not allow for data decryption.
- Private key: This key should be strictly protected, as anyone who possesses it can decrypt the data.
When communicating with a server via a secure SSL connection, the browser encrypts the data being sent using the public key. From that moment on, only the web server that has the private key is able to decrypt the data and see what was sent.
Generating an SSL certificate
When generating an SSL certificate, a private key is created, which is required to install the SSL certificate on the server. The private key is generated only once; if it’s lost, you can only request a new SSL certificate.
The process of issuing a free certificate in cPanel is fully automated, and the appropriate scripts add the SSL certificate key to the server’s configuration. In the case of a purchased, paid SSL certificate, you must install the key and the certificate yourself.
RSA or ECDSA encryption?
SSL certificates with ECDSA key encryption are a newer solution and are slowly becoming more popular than certificates with RSA key encryption.
Both types of encryption are equally secure, and you can continue to use RSA-encrypted certificates without any concerns about the safety of your data.
At the time of writing this article, Smarthost.au servers have implemented SSL certificates with the newer key encryption method, namely ECDSA encryption.
- Clearing redis cache memory - December 22, 2022
- Does “Time to first byte” (TTFB) means server speed? - October 31, 2022
- Automatic WordPress login security by reCaptcha - August 24, 2021

